 This post is co-authored by Dr. Kyle Harrison (@KyleHarrisonMD) and has also been featured on CSA Online First.
This post is co-authored by Dr. Kyle Harrison (@KyleHarrisonMD) and has also been featured on CSA Online First.
So, you’ve finished your third year of medical school and have decided that you want to be an anesthesiologist. In our completely biased opinion, you are making the right choice and, at the end of your residency training, you will be in a unique position to enhance the experience and improve the outcomes of patients undergoing surgery and invasive procedures. However, securing a coveted slot in an anesthesiology residency in the United States has never been more competitive. In the many years that we have spent as faculty in academic anesthesiology departments, we have learned a few things about the application process. Our views are our own and do not reflect the official views of any anesthesiology residency program with which we have been affiliated. The following are some (hopefully helpful) answers to common questions that we have been asked over the years.
How High Do My USMLE Score and GPA Have to Be?
Competitive scores are essential. We can’t quote you a number because they vary year to year and program to program, but the trend is only increasing. All medical students, regardless of school, applying in anesthesiology must do well on the USMLE. Think about it — this is the only equalizing factor between schools that teach differently or have different reputations. Having a great score doesn’t guarantee you admission, but if your scores are not competitive, you will have an uphill battle to get a residency slot at a top program. The value of the standardized test score in learning is often debated in academia; however, no one will argue against the conclusion that previous success on standardized tests usually predicts future success on standardized tests. Residency training is demanding. Programs want their residents 100 percent committed and not worrying too much about how they will perform on their annual in-training exams and eventual certification exam.
Do I Need to Have Research Experience?
No program will ever discourage applicants with research experience from applying; we would say that it is not required but is recommended. Don’t do it for the sake of doing it, but definitely do it if you can find a project that you are passionate about. While research in anesthesiology or pain makes sense (shows academic interest in the chosen field), it can really be in any area. It is more impressive to be involved in a project (big or small), see it through, and maybe even present at a meeting or publish in a journal, than to just say you did “research.” If you do list research on your application or curriculum, make sure you can talk about the project, your specific role, and what you learned from it; you will be asked. If you are not interested in research, then consider focusing on another aspect of extracurricular life such as community service.
What Should Be on My List of Extracurricular Activities?
If there is something about you that is really different, it’s helpful to mention it. Again, the application process isn’t perfect, but the file you submit is all the information program coordinators and directors have. If you have done something special — climbed Mt. Everest, set up HIV clinics in Africa, won Olympic medals, had a previous career — or do something noteworthy, such as volunteer extensively in your community, play an instrument, or dance professionally, mention those things. Yes, we have actually seen these applicants (and interviewed them of course)! Selection committee members often apply the “3 a.m. call rule” when reviewing an applicant. This is: Would you like to be on call in the middle of the night with this person? Applicants viewed as hardworking, clinically competent, and interesting to talk to should result in a solid “yes.” If you just like to run in your free time, mentioning that probably doesn’t make a huge difference in the application.
Do I Need to Do an Anesthesiology Rotation?
You should do an anesthesiology rotation at your local institution at the very least. Programs want to know if you understand what you’re getting yourself into. And it does make a difference how well you did on the rotation. Many students approach their anesthesiology rotation as the “intubation and IV insertion” rotation. Most anesthesiologists like us are passionate about their specialty, and the specialty itself in rapidly evolving (familiarize yourself with the Perioperative Surgical Home model). Trust us — we can tell when a student is genuinely interested in anesthesiology, or not. In our experience, medical students who stand out pay attention to what is going on in the perioperative period, anticipate events, know how to be helpful, get involved with the entire patient care episode (starting with the preoperative evaluation, through giving report to the nurse in the recovery room, and even including postoperative follow-up). It is never impressive to see a medical student standing around looking bored. There is always something to do — for example, when a patient arrives in the OR, you can start applying monitors without prompting, or help with positioning. Residents and staff anesthesiologists recognize these things and reward you by getting you more involved with patient care, including procedures.
Who Should Write My Letters of Recommendation?
The dean’s letter is the big one and counts the most. The form of the dean’s letter is usually standardized, so residency program directors have to weed through all the verbiage to get the information they want. It helps when the dean’s letter includes the student’s rank and any special merits (e.g., AOA). Additional letters should be written by faculty members who really know you and can provide helpful content — research mentor, career advisor, staff physician with whom you have worked closely. It doesn’t add strength to an application to have a lot of generic letters (quality over quantity); three strong letters are better than two strong plus three average letters, since the strong letters may get lost in the sea of information in the applicant’s file.
What Else Can I Do to Improve My Chances?
Unfortunately there are no guarantees. The “gatekeeper” is the initial electronic application. With anesthesiology departments receiving hundreds of applications each year, most will sound exactly the same. “I love pharmacology and physiology” (while possibly true for some) only takes you so far. Something unique about the applicant has to come through the pages. Excellent grades and USMLE scores, strong dean’s letter and other recommendations, personal experiences, prior careers, other degrees, thought-provoking research, a list of activities, and a unique personal statement — anything that sets you apart from the pack can make a difference!


 re administering a medication, it’s not enough just to understand the complex pharmacologic effects of the drug and determine the right dose. The anesthesiologist also has to know how to dilute and prepare the drug, the appropriate route for the medication, which other medications are and are not compatible, and how to program the infusion device. In addition, an anesthesiologist has to be technically skilled at finding veins—sometimes in the hand or arm, sometimes leading centrally to the heart—in order to give the medication in the first place.
re administering a medication, it’s not enough just to understand the complex pharmacologic effects of the drug and determine the right dose. The anesthesiologist also has to know how to dilute and prepare the drug, the appropriate route for the medication, which other medications are and are not compatible, and how to program the infusion device. In addition, an anesthesiologist has to be technically skilled at finding veins—sometimes in the hand or arm, sometimes leading centrally to the heart—in order to give the medication in the first place.
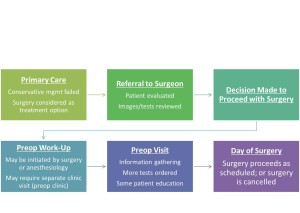
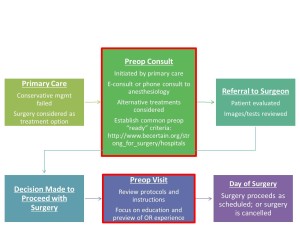
 ternet, it is more important than ever for us to reach out to them.
ternet, it is more important than ever for us to reach out to them.