Guest post by Seshadri Mudumbai, MD, MS. Dr. Mudumbai is an Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine at Stanford University School of Medicine. He is also a health services researcher and physician anesthesiologist at the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
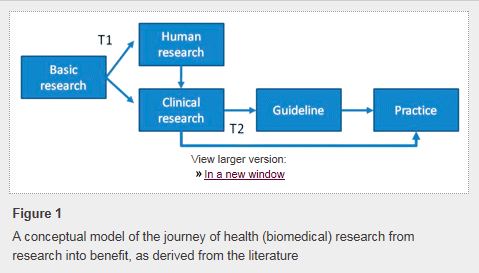
 Changing physician behavior is rarely easy, and studies show that it can take an average of 17 years before research evidence becomes widely adopted in clinical practice. One study published in JAMA has identified 7 categories of change barriers:
Changing physician behavior is rarely easy, and studies show that it can take an average of 17 years before research evidence becomes widely adopted in clinical practice. One study published in JAMA has identified 7 categories of change barriers:
- Lack of awareness (don’t know guidelines exist)
- Lack of familiarity (know guidelines exist but don’t know the details)
- Lack of agreement (don’t agree with recommendations)
- Lack of self-efficacy (don’t think they can do it)
- Lack of outcome expectancy (don’t think it will work)
- Inertia (don’t want to change)
- External barriers (want to change but blocked by system factors)
Why Change?
According to the Institute of Medicine’s Crossing the Quality Chasm: a New Health System for the 21st Century: “Patients should receive care based on the best available scientific knowledge. Care should not vary illogically from clinician to clinician or from place to place.” Our group has focused our efforts on implementing updated evidence-based medicine initiatives for surgical patients with a special emphasis on the total knee replacement population. Knee replacement is already one of the most common types of surgery in the United States (over 700,000 procedures per year). Given an aging population, the volume of knee replacement surgeries is expected to increase to over 3 million by the year 2030.
We now have sufficient evidence to support “neuraxial anesthesia” (such as a spinal or epidural) as the preferred intraoperative anesthetic technique for knee replacement patients. With neuraxial anesthesia, an injection in the back temporarily numbs the legs and allows for painless surgery of the knee. Several studies have now shown better outcomes and fewer complications after knee replacement surgery with neuraxial anesthesia when compared with general anesthesia. Despite these known benefits, a large study evaluating data from approximately 200,000 knee replacement patients across the United States reveals that use of neuraxial anesthesia occurs in less than 30% of cases. At our facility prior to changing our practice, we noted a 13% rate of neuraxial anesthesia utilization. In the face of growing evidence, we chose to change our practice, and the results of these efforts are reported in our recently published article.
How Did We Start?
An important tool used to coordinate the perioperative care of knee replacement patients has long been the clinical pathway. A clinical pathway is a detailed care plan for the period before, during, and after surgery that covers multiple disciplines: surgery, anesthesiology and pain management, nursing, physical and occupational therapy, and sometimes more. The concept of the clinical pathway should be dynamic and not static. This requires a process to ensure clinical pathways are periodically updated and someone to take a leadership role in managing the process.
At our institution, we established a coordinated care model known as the Perioperative Surgical Home (PSH). The PSH provides the overall structure and coordination for perioperative care, and multiple clinical pathways exist within this structure. With a PSH, physician anesthesiologists are charged with providing leadership and oversight of specific clinical pathways, collecting and reviewing data, engaging frontline healthcare staff and managers across disciplines, and suggesting changes or updates to clinical pathways as new evidence emerges.
Within our PSH model, we invested in a 5 month process to change our preferred anesthetic technique from general anesthesia to neuraxial anesthesia within the clinical pathway for knee replacement patients. This process involved many steps and followed the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research:
- Literature review and interdepartmental presentation
- Development of a work document
- Training of staff
- Prospective collection of data with feedback to staff.
After one year, the overall percentage of knee replacement patients receiving neuraxial anesthesia increased to 63% from 13%, and a statistically-significant increase in neuraxial anesthesia use took place within one month of the updated clinical pathway rollout.
How Do We Keep It Going?
Neuraxial anesthesia continues to be the predominant anesthetic technique that our knee replacement patients receive today. We attribute the ongoing success of this change to multidisciplinary collaboration, physician leadership in the form of a departmental champion, peer support and feedback, frequent open communication, and engagement and support from facility leadership. The results of our study and experience show that a PSH may help facilitate changes in clinical practice quicker than other less-coordinated models of care. As PSH models continue to be developed, further evidence to support the impact of clinical practice changes on patient-oriented outcomes related to quality and safety and healthcare economics is needed.
For patient education materials regarding anesthetic options for knee replacement surgery, please visit My Knee Guide.